Pepsi Cola Nutrition Facts A Detailed Look
Pepsi Cola Ingredients & Their Nutritional Impact
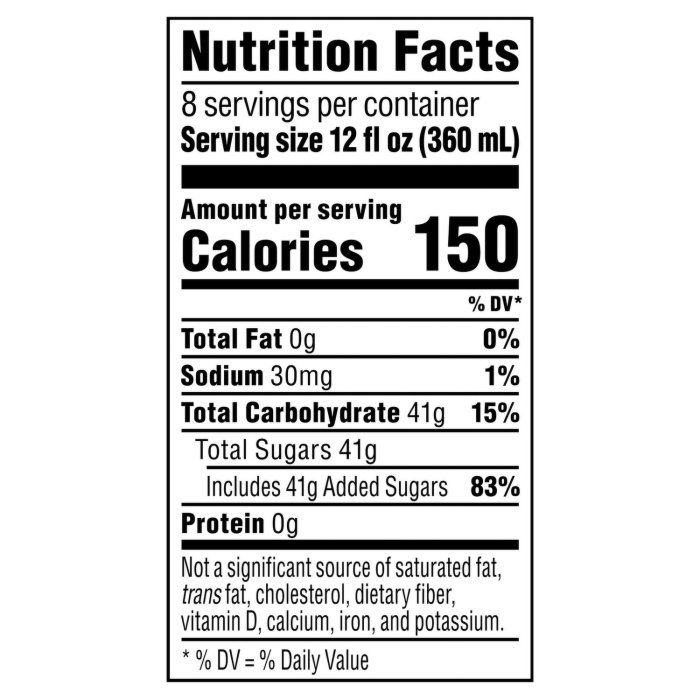
Pepsi cola nutrition facts – The ephemeral nature of pleasure, like the fleeting fizz of a Pepsi, often masks a deeper truth about its composition. Understanding the ingredients within this ubiquitous beverage allows us to cultivate a mindful relationship with consumption, a journey toward a more balanced and enlightened existence. This exploration delves into the nutritional impact of Pepsi Cola, examining its components and their subtle yet significant effects on our well-being.
Nutritional Breakdown of Pepsi Cola
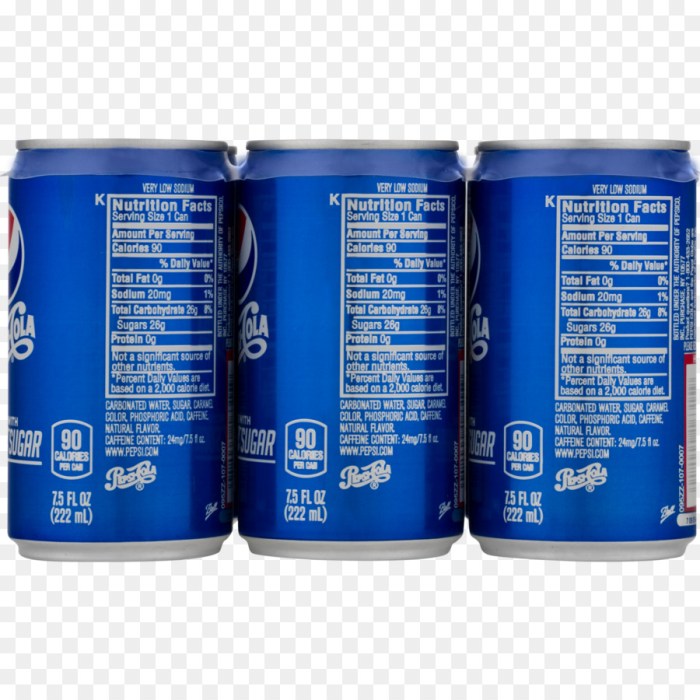
A typical 355ml serving of Pepsi Cola contains approximately 150 calories, 40 grams of carbohydrates (almost all of which are sugars), 0 grams of fat, and 0 grams of protein. This simple breakdown, however, belies the complex interplay of ingredients within the beverage. The dominant component is sugar, predominantly high-fructose corn syrup, which provides the sweetness and contributes significantly to the caloric density.
Artificial sweeteners, while present in some diet versions, offer a different set of considerations regarding their long-term effects. Preservatives, such as phosphoric acid, help maintain the shelf life but also impact the overall acidity of the drink.
The Health Effects of Pepsi Cola Ingredients
Sugar’s role in contributing to weight gain, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders is well-documented. The high concentration of sugar in Pepsi, derived primarily from high-fructose corn syrup, represents a significant contributor to these health risks. While artificial sweeteners like aspartame or sucralose provide a calorie-free alternative, their potential long-term health implications remain a subject of ongoing research and debate, raising questions about their overall impact on the body’s metabolic processes.
The phosphoric acid present acts as a preservative and contributes to the drink’s characteristic tartness; however, excessive consumption of acidic beverages can contribute to tooth enamel erosion.
Comparison with Similar Carbonated Beverages
Many other carbonated beverages share a similar composition to Pepsi Cola, with variations in the type and amount of sweeteners, preservatives, and flavorings. For example, Coca-Cola utilizes a different blend of sweeteners and flavorings, resulting in a slightly different taste profile and nutritional composition. Other brands may opt for different artificial sweeteners or natural sweeteners like stevia, altering both the taste and nutritional impact.
These subtle differences, while seemingly minor, highlight the complexity of navigating the choices available in the market.
Nutritional Information Per Serving (355ml)
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 150 |
| Carbohydrates | 40g |
| Sugars | 40g |
| Protein | 0g |
| Fat | 0g |
Pepsi Cola and Dietary Guidelines

The path to mindful consumption lies in understanding the interplay between our choices and our well-being. Pepsi Cola, a ubiquitous beverage, presents a compelling case study in this delicate balance. By examining its nutritional profile against established dietary guidelines, we can gain valuable insights into the impact of regular consumption and how to integrate it, if at all, into a holistic and balanced lifestyle.Pepsi Cola’s nutritional composition, predominantly high in sugar and carbohydrates, necessitates careful consideration within the framework of recommended daily intakes.
Pepsi Cola’s nutritional profile, dominated by sugar and lacking substantial nutritional value, starkly contrasts with the comparatively higher protein and fat content found in other food choices. A look at the nutritional breakdown of foods like cheddar cheese nutrition facts reveals a different nutritional landscape altogether, highlighting the varied impact of food choices on overall health. Ultimately, understanding the nutritional details of Pepsi, and contrasting it with alternatives, is crucial for informed dietary decisions.
Understanding these guidelines allows us to make conscious choices that support our physical and spiritual equilibrium.
Comparison of Pepsi Cola to Dietary Guidelines
Dietary guidelines generally recommend limiting added sugar intake to less than 10% of total daily calories. A typical 12-ounce can of Pepsi Cola contains approximately 40 grams of sugar, which translates to a significant portion of this recommended limit, particularly for individuals with lower daily caloric needs. Similarly, carbohydrate intake should be balanced, focusing on complex carbohydrates rather than the simple sugars found in abundance in Pepsi Cola.
Excessive consumption can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain. The absence of essential vitamins and minerals further underscores the need for moderation. In contrast, a balanced diet emphasizes nutrient-dense foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, providing sustained energy and supporting overall health.
Implications of Regular Pepsi Cola Consumption
Regular consumption of Pepsi Cola, exceeding recommended daily sugar and carbohydrate limits, can contribute to several health concerns. These include weight gain, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and dental problems. The lack of essential nutrients further compromises overall nutritional balance. Consider, for example, the case of an individual consuming two or more cans of Pepsi Cola daily.
Their sugar intake significantly surpasses recommended levels, potentially leading to long-term health complications. This underscores the importance of mindful consumption and the need to prioritize nutrient-rich options.
Incorporating Pepsi Cola into a Balanced Diet Plan (Hypothetical Example)
While not a cornerstone of a healthy diet, Pepsi Cola can be occasionally incorporated in moderation as part of a carefully planned approach. Consider a hypothetical individual aiming for a 2000-calorie diet with a recommended sugar intake of no more than 50 grams. They could allocate a small portion of their daily sugar allowance to a single 12-ounce can of Pepsi Cola, but only if the remaining dietary choices are rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
This approach emphasizes the importance of balance and mindful choices, prioritizing nutrient-dense foods while allowing for occasional indulgences within a carefully calculated framework.
Comparative Nutritional Profile of Beverages
| Beverage | Sugar (g/12 oz) | Calories (12 oz) | Other Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pepsi Cola | 40 | 150 | Minimal |
| Water | 0 | 0 | None |
| Unsweetened Tea | 0 | 0-5 | Antioxidants (depending on type of tea) |
| 100% Fruit Juice (4 oz) | Variable (check label) | Variable (check label) | Vitamins, Minerals |
Visual Representation of Pepsi Cola Nutrition Facts

A compelling visual representation of Pepsi Cola’s nutritional information can transcend mere data presentation, becoming a powerful tool for mindful consumption. By transforming complex numbers into easily digestible graphics, we can foster a deeper understanding of the beverage’s composition and its potential impact on our well-being. This allows for a more informed choice, aligning personal decisions with a holistic approach to health.Consider a bar graph, a universally understood visual format.
This graph could depict the percentage contribution of each macronutrient – carbohydrates, proteins, and fats – to the total caloric content of a serving of Pepsi Cola. The dominant presence of carbohydrates, represented by a significantly larger bar, would immediately highlight their primary role in the beverage’s energy profile. The near absence of protein and fat would be equally clear, visually emphasizing the beverage’s limited contribution to these essential macronutrients.
Such a representation provides an immediate, intuitive grasp of the nutritional profile, far exceeding the impact of a simple numerical list.
Creating an Infographic Summarizing Pepsi Cola’s Nutritional Aspects, Pepsi cola nutrition facts
An infographic offers a potent means to communicate the key nutritional aspects of Pepsi Cola in a concise and engaging manner. The design should prioritize clarity and visual appeal to effectively convey complex information.A vibrant, yet clean color scheme would be crucial. Using a color palette that evokes both energy and health consciousness, perhaps incorporating shades of blue (associated with refreshment) and green (associated with natural elements), can create a balanced and appealing visual experience.
The chosen color scheme should also aid in differentiating data points; for example, the bar representing carbohydrates could be a lighter shade of blue, while the nearly insignificant bars for protein and fat could be a darker shade of blue or a different color entirely to highlight the contrast.Clear and easily readable fonts are essential. A sans-serif font, such as Arial or Helvetica, is recommended for its readability across different sizes and media.
The font size should be appropriately scaled to ensure readability, with titles and headings using a larger font size than body text.Data visualization should leverage the strengths of the bar graph, as previously discussed, but also include other elements to enhance understanding. For instance, a pie chart could illustrate the percentage contribution of sugars to the total carbohydrate content, offering a more granular view of the beverage’s sugar composition.
Small icons representing key nutrients (or lack thereof) could be incorporated alongside the numerical data, providing a visual cue that reinforces the numerical information. For instance, a small icon depicting a sugar crystal could be placed next to the sugar content data point. Finally, a concise summary of the key takeaways, such as “High in Sugar, Low in Nutrients,” could be prominently displayed to leave a lasting impression.
This multi-faceted approach, combining multiple visual representations with a well-defined color scheme and clear typography, ensures that the infographic effectively communicates the essential nutritional information in a memorable and easily understood manner.
FAQ Explained
Is Pepsi Cola suitable for weight loss diets?
No, due to its high sugar and calorie content, Pepsi Cola is generally not recommended for weight loss diets. It’s best to opt for water, unsweetened tea, or other low-calorie alternatives.
Does Pepsi Cola contain caffeine?
Yes, Pepsi Cola contains caffeine, though the exact amount varies slightly depending on the region and formulation.
Are there sugar-free versions of Pepsi Cola?
Yes, Pepsi offers diet and zero-sugar versions sweetened with artificial sweeteners. However, it’s important to be aware of the potential long-term health implications of artificial sweeteners.
What are the potential long-term effects of regular Pepsi consumption?
Regular consumption of Pepsi, due to its high sugar content, can contribute to weight gain, type 2 diabetes, tooth decay, and other health problems. Moderation is key.
