Apple Cider Vinegar Nutrition Facts A Deep Dive
Health Benefits Associated with Apple Cider Vinegar Consumption
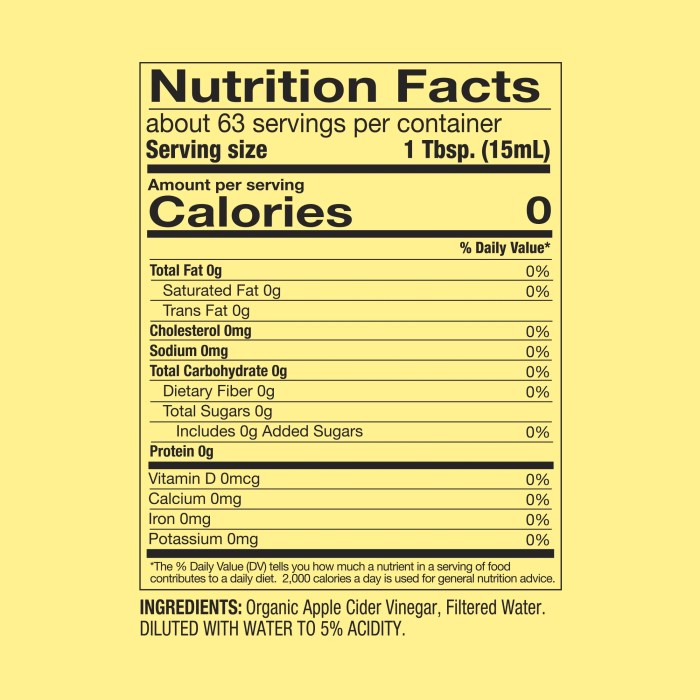
Apple cider vinegar nutrition facts – Apple cider vinegar (ACV), a fermented product of apples, has gained popularity for its purported health benefits. While research is ongoing and more robust studies are needed to confirm many claims, several potential advantages have been explored, focusing on its impact on blood sugar control and weight management. It’s crucial to remember that ACV is not a miracle cure and should be used as part of a holistic approach to health, always consulting with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
Apple Cider Vinegar and Blood Sugar Control
Several studies suggest that ACV may have a positive impact on blood sugar regulation. The mechanisms are not fully understood, but it’s hypothesized that ACV may improve insulin sensitivity and slow down the rate at which glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream. For instance, a study published in the
- Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry* found that consuming ACV before a high-carbohydrate meal resulted in lower postprandial blood glucose levels in participants. Another study, published in
- Diabetes Care*, showed that regular ACV consumption improved insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes. These findings suggest a potential role for ACV in managing blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals at risk of or diagnosed with diabetes. However, it’s important to note that the effects can vary depending on factors like the dose of ACV consumed, the individual’s metabolic profile, and the presence of other underlying health conditions.
Apple cider vinegar boasts a low calorie count and offers trace amounts of vitamins and minerals. However, its nutritional profile pales in comparison to fermented beverages like kombucha. For a contrasting example, consider the nutritional information available for pineapple sunset hard kombucha nutrition facts , which often lists carbohydrates and probiotics. Ultimately, both apple cider vinegar and kombucha contribute differently to a balanced diet.
More research is needed to fully elucidate the relationship between ACV consumption and blood sugar control.
Apple Cider Vinegar and Weight Management, Apple cider vinegar nutrition facts
The potential of ACV for weight management is another area of interest. Some studies suggest that ACV may contribute to weight loss by increasing feelings of fullness, reducing calorie intake, and potentially boosting metabolism. For example, research has indicated that consuming ACV can increase satiety hormones, leading to a decrease in overall food consumption. Additionally, some studies have shown a modest association between ACV consumption and reduced body weight and body fat percentage.
The mechanisms involved are likely multifaceted, potentially including effects on gut microbiota, improved insulin sensitivity, and increased fat burning. However, it’s crucial to emphasize that ACV alone is unlikely to result in significant weight loss without a comprehensive approach encompassing a balanced diet and regular exercise. The observed effects are often modest and may vary greatly between individuals.
Comparison of Apple Cider Vinegar with Other Vinegar Types
While apple cider vinegar is often highlighted for its health benefits, other vinegar types, such as white vinegar and red wine vinegar, also possess some nutritional value and may offer similar, albeit potentially less pronounced, effects. All vinegars are sources of acetic acid, the main active compound believed to be responsible for many of the purported health benefits. However, apple cider vinegar is often favored due to its additional components, including “mother,” a cloudy substance containing beneficial bacteria and enzymes.
The presence of these components is thought to contribute to its purported enhanced health benefits compared to other vinegar types. Further research is needed to definitively compare the health impacts of different vinegar types and to isolate the specific components responsible for observed effects. The potential benefits of other vinegar types remain an area of ongoing investigation.
Apple Cider Vinegar vs. Other Health Tonics: Apple Cider Vinegar Nutrition Facts

Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has gained popularity as a health tonic, but it’s important to understand how its nutritional profile and purported benefits compare to other commonly used beverages. This comparison helps to contextualize ACV within a broader range of wellness choices, allowing for a more informed decision about its inclusion in a healthy lifestyle. Understanding the nuances of each tonic’s impact can contribute to a more balanced and effective approach to overall well-being.
Comparative Analysis of Health Tonics
The following table provides a comparison of apple cider vinegar with lemon water and ginger tea, highlighting key nutrients, claimed benefits, and potential side effects. It’s crucial to remember that the claimed benefits are often anecdotal and require further rigorous scientific investigation. Individual responses to these tonics can also vary significantly.
| Tonic | Key Nutrients | Claimed Benefits | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple Cider Vinegar | Acetic acid, potassium, pectin (small amounts of vitamins and minerals) | Improved digestion, blood sugar control, weight management (evidence is limited and often contradictory), potential antimicrobial properties. | Tooth enamel erosion, heartburn, interactions with medications (e.g., diuretics, insulin), low blood potassium levels in large quantities. |
| Lemon Water | Vitamin C, potassium, antioxidants | Hydration, improved digestion, boosted immunity (Vitamin C contributes to immune function), potential aid in weight management (due to satiety). | Tooth enamel erosion (acidic), potential for heartburn in sensitive individuals. |
| Ginger Tea | Gingerols (anti-inflammatory compounds), antioxidants, small amounts of vitamins and minerals | Relief from nausea and indigestion, anti-inflammatory effects, potential pain relief. | Heartburn, interactions with blood thinners, potential allergic reactions. |
Nutritional Differences Between Beverages
The nutritional content of ACV, lemon water, and ginger tea differs significantly. ACV’s primary nutritional component is acetic acid, which contributes to its purported health benefits but also to its potential side effects. Lemon water is rich in Vitamin C and potassium, offering hydration and antioxidant benefits. Ginger tea provides gingerols, known for their anti-inflammatory properties. All three beverages contribute minimally to overall daily vitamin and mineral intake compared to a balanced diet.
For example, while ACV contains trace amounts of potassium, it pales in comparison to the potassium found in a banana. Similarly, the Vitamin C in lemon water is not as concentrated as in a serving of oranges. The antioxidant content varies depending on the quality and preparation of the beverage, with ginger tea potentially offering a higher concentration of antioxidants than the other two.
Question Bank
Is apple cider vinegar safe for everyone?
While generally safe for most people in moderation, individuals with certain health conditions (e.g., low potassium levels, dental problems) should consult their doctor before regular consumption.
Can apple cider vinegar help with digestion?
Some anecdotal evidence suggests it may aid digestion, but more research is needed to confirm these claims. Its acidity can irritate existing digestive issues for some.
How should I store apple cider vinegar?
Store it in a cool, dark place in a tightly sealed container to maintain its quality and prevent spoilage.
Does apple cider vinegar interact with any medications?
Yes, it can interact with certain medications, particularly those affecting blood sugar or potassium levels. Consult your doctor if you’re on medication.
